



South African feed market continues optimisation
Poultry represents a large part of the feed sectorThe South African animal feed industry can be divided into three important groups, namely the feed manufacturers (dedicated processors of feed for direct sales), the feedlot sector, and informal feed milling, according to a recent US Department of Agriculture (USDA) Global Agricultural Information Network (GAIN) report.
Feed manufacturers can further be divided into balanced feed manufacturers and pre-mix manufacturers. The local feed manufacturers are represented by the Animal Feed Manufacturing Association (AFMA).
The feed manufacturers contribute to most feed sales in South Africa and represent about 60% of South Africa’s total animal feed production of approximately 13 million metric tons (MMT).
Feed manufactures play a particularly important role in the poultry industry. The South African poultry industry is highly concentrated and dominated by vertically integrated companies with the five major players producing approximately 70% of local poultry.
These vertically integrated businesses produce significant volumes of feed for internal consumption and sell the excess to non-integrated poultry producers. Key activities include the manufacturing of animal feed, broiler genetics, production and sale of day-old chicks and hatching eggs, breeder and broiler production, abattoir and further processing operations and sales and distribution of various key poultry brands. This model, which connects the entire production chain from the breeders, feed mills, farms and hatcheries to the processing plants, is essential for achieving economies of scale.
Feed produced by the feedlots is used as an on-farm input and does not necessarily end up in the general animal feed market. The feedlot sector is an intensive production system with the goal of growing and fattening livestock for slaughter. The feedlot industry produces approximately 75% of all beef products consumed in South Africa. The South Africa Feedlot Association (SA Feedlot) represents the approximately 100 locally operated feedlots. Informal feed milling is done on-farm, and the feed is mainly for own use.
The animal feed manufacturers source various raw materials, including primary commodities and by-products from processing, to manufacture scientifically formulated feed for specific animals. The major primary commodities used are corn (primarily yellow corn), oilseeds (mostly full-fat soybeans), and other grains and dry materials such as hay. By-products from processing used as inputs for animal feed include oilseed meals (from oil crushing), various flour, germ, and hulls (from grain milling), molasses & bagasse (from sugar processing), and animal & fish meal (from meat processing). Additional products are sourced from mining (limestone & phosphates) and chemical manufacturing (vitamins & medicine).
Each manufactured feed follows strict formulations based on the nutritional requirements of various animals. For every animal type, different feed products are developed to support optimised development within the different growth stages of the animal.
The market for manufactured feed is given on the far right of Table 1 and Figure 5 and includes poultry, dairy, beef, sheep, and pigs.
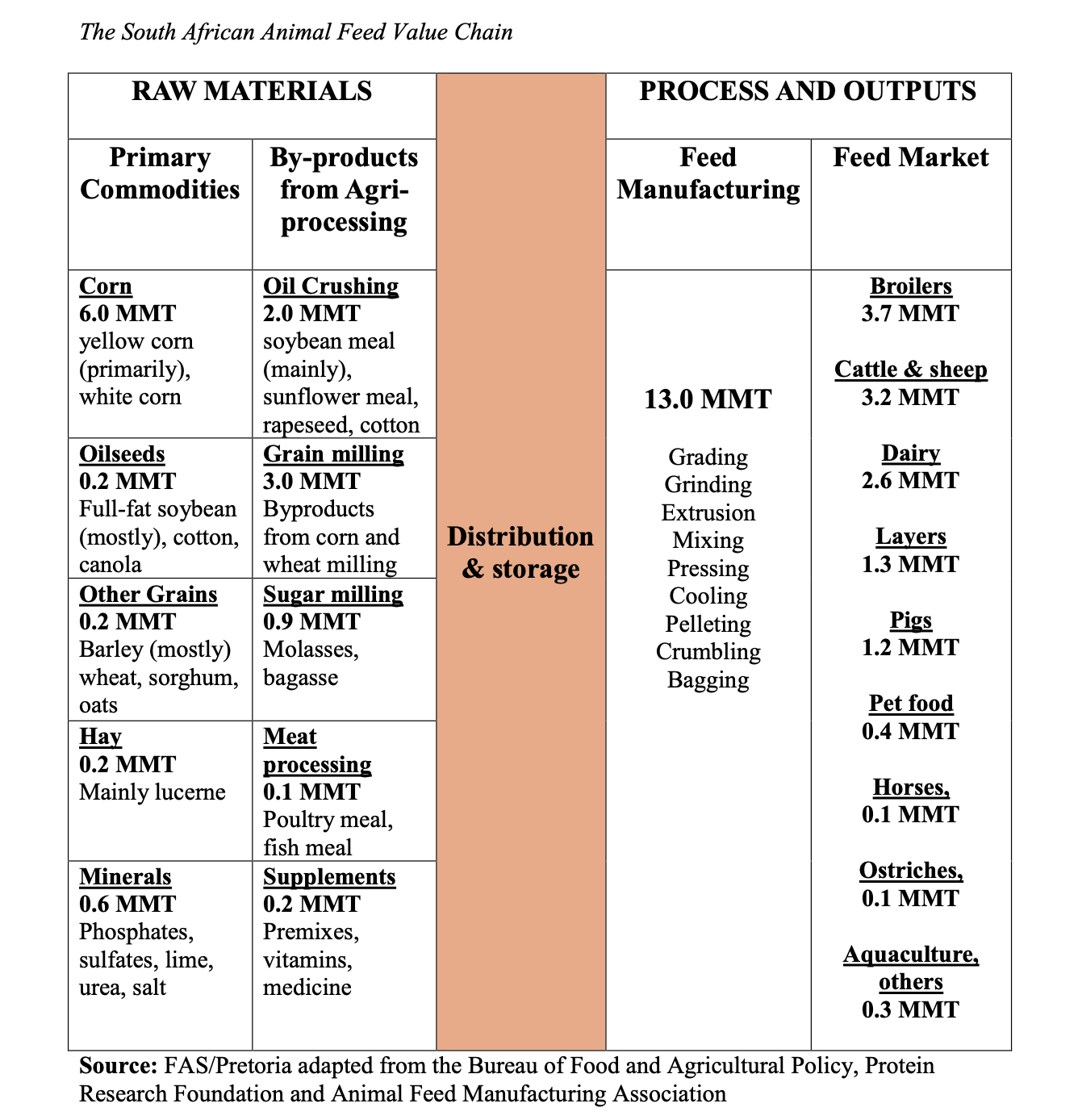
The importance of the poultry industry is clear, with broiler and layer feed representing 40% of total feed sales totalling more than 5 MMT. The poultry industry is followed by feed for cattle and sheep feedlots (3.2 MMT), dairy (2.6 MMT), and pigs (1.2 MMT).




